
DIFFRACTIVE DIFFUSION PLATES (LSD)
Optcom Diffusion Plates Not Only Diffuse Light But Also are Available in Each Diffusion Level, Which Makes Them Ideal for Adjusting Light Quantity When Measuring Light Source Optical Characteristics.
Ideal for light intensity adjustment. 5 types available depending on the degree of diffusion.
OVERVIEW

Diffusion plates are used to scatter light from the light source to obtain uniform light with no variations in light quantity and in this way help improve repeatability especially when reproducing light in light source color measurements. Diffractive diffusion plates called LSD or light shaping diffusers from hereon, act to suppress light diffusion during color measurement more than ND filters or conventional diffraction plates. LSD can also vary the light quantity by changing their divergence angle
FEATURES
- (1) Gives Same Effect As a Lens
-
Randomly placed micron level surface structures made by surface relief hologram patterning render the same effect as a micro-concave lens array. These structures diffuse the light with a diffracting effect.
- (2) Light Source Can be Freely Selected As Needed
-
These LSD are not wavelength dependent and so are usable on all types of light sources including laser light, white light and LED light. LSD can freely shape even coherent and incoherent light by diffusion into spherical, elliptical or rectangular shapes.
- (3) High Transmittance Rate
-
LSD allow high light transmittance of 85% to 92% at wavelengths from 365 to 1600 nm and fully utilize the light source power (transmittance rate varies with factors such as plate thickness, material transmittance, and added options, etc.).
- (4) Light Distribution Control
-
Input light is distributed (diffused) along a preset range to simultaneously produce highly uniform light. Though most effective on parallel light, LSD also work well on light sources having a divergent angle.
DIAGRAM
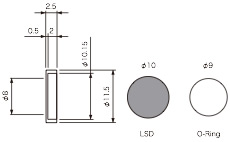
SPECIFICATIONS
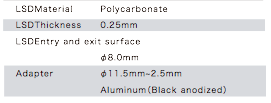
LINEUP
Product lineup of 5 types with different diffusion angles. LSD diffusion angles are designed assuming the diffusion angle which occurs when input with parallel light such as from a laser. This means the light scatters in widely diverging angles if using the LSD in light sources having their own divergence angle such as an LED or halogen light source.
LSD Versus Ordinary Diffusion Plates

Groove surfaces having tiny irregularities of about 5 micrometers are formed on the surface plate of the LSD by hologram patterning, so the light divergence angle can be freely set as needed. These are also designed to keep non-periodic moiré stripes and color deviations from occurring. Combining this LSD for example with a lamp type LED having a selectable divergence angle yields a stable diffusion angle and attains high light density (boosts the transmittance rate).
Ordinary diffusion plates on the other hand are polished by sandblasting a grid on the plate (sapphire or quartz, BK7, etc.) according to its roughness to form a matte (non-shiny state). This polishing is usually in one direction and even supposedly high precision diffusion plates are mostly polished in only 2 directions up/down and left/right. This means the diffuser surface is orientated in a set direction so that the diffusing light might cause problems such as moiré stripes and color deviations.
Transmittance Rates at Different LSD Diffusion angles
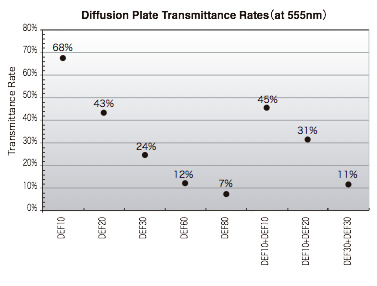
The LSD transmittance rate varies with its plate divergence angle. The LSD diffusion angle is the same or larger than Frost type diffusion plates so luminous quantity can be adjusted by combining the divergence angles. The following graph given for reference shows transmittance rates measured during irradiation of halogen light onto 1 LSD plate at each divergence angle.




